Ambient
Showing 140701–140750 of 146505 results
-

TNF-α, Human (P. pastoris-expressed)
$612.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune diseases. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases including Crohn’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis as well as graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-α, Human (P. pastoris-expressed)
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune diseases. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases including Crohn’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis as well as graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-α, Human (P. pastoris-expressed)
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune diseases. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases including Crohn’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis as well as graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-α, Mouse
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) is produced by neutrophils, activated lymphocytes, macrophages, NK cells, LAK cells, astrocytes endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells and some transformed cells. Mouse TNF-α occurs as a membrane-anchored form. The naturally-occurring form of TNF-α is glycosylated, but non-glycosylated recombinant TNF-α has comparable biological activity. The biologically active native form of TNF-α is reportedly a trimer. Human and mouse TNF-α show approximately 79% homology at the amino acid level and crossreactivity between the two species.
-

TNF-α, Mouse (P. pastoris-expressed)
$1,177.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) is produced by neutrophils, activated lymphocytes, macrophages, NK cells, LAK cells, astrocytes endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells and some transformed cells. Mouse TNF-α occurs as a membrane-anchored form. The naturally-occurring form of TNF-α is glycosylated, but non-glycosylated recombinant TNF-α has comparable biological activity. The biologically active native form of TNF-α is reportedly a trimer. Human and mouse TNF-α show approximately 79% homology at the amino acid level and crossreactivity between the two species.
-

TNF-α, Mouse (P. pastoris-expressed)
$254.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) is produced by neutrophils, activated lymphocytes, macrophages, NK cells, LAK cells, astrocytes endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells and some transformed cells. Mouse TNF-α occurs as a membrane-anchored form. The naturally-occurring form of TNF-α is glycosylated, but non-glycosylated recombinant TNF-α has comparable biological activity. The biologically active native form of TNF-α is reportedly a trimer. Human and mouse TNF-α show approximately 79% homology at the amino acid level and crossreactivity between the two species.
-

TNF-α, Mouse (P. pastoris-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) is produced by neutrophils, activated lymphocytes, macrophages, NK cells, LAK cells, astrocytes endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells and some transformed cells. Mouse TNF-α occurs as a membrane-anchored form. The naturally-occurring form of TNF-α is glycosylated, but non-glycosylated recombinant TNF-α has comparable biological activity. The biologically active native form of TNF-α is reportedly a trimer. Human and mouse TNF-α show approximately 79% homology at the amino acid level and crossreactivity between the two species.
-
TNF-α, Porcine
$668.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune disease. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune disease including Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis and graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-α, Porcine
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune disease. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune disease including Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis and graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-α, Porcine
$90.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune disease. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune disease including Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis and graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-α, Rat
$953.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune disease. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune disease including Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis and graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-α, Rat
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune disease. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune disease including Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis and graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-α, Rat
$133.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune disease. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune disease including Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis and graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-β, Human
$1,323.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsTNF is secreted by macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, T-cells, NK-cells following their stimulation by bacterial LPS. Cells expressing CD4 secrete TNF-alpha while CD8 cells secrete little or no TNF-alpha. The synthesis of TNF-alpha is induced by many different stimuli including interferons, IL2, GM-CSF. TNF-β is a potent mediator of inflammatory and immune responses. It belongs to the TNF family of ligands, and signals through TNFR1 and TNFR2. TNF-β is produced by activated T and B lymphocytes, and has similar activities to TNF-α. It mediates a large variety of inflammatory, immunostimulatory, and antiviral responses.
-

TNF-β, Human
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsTNF is secreted by macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, T-cells, NK-cells following their stimulation by bacterial LPS. Cells expressing CD4 secrete TNF-alpha while CD8 cells secrete little or no TNF-alpha. The synthesis of TNF-alpha is induced by many different stimuli including interferons, IL2, GM-CSF. TNF-β is a potent mediator of inflammatory and immune responses. It belongs to the TNF family of ligands, and signals through TNFR1 and TNFR2. TNF-β is produced by activated T and B lymphocytes, and has similar activities to TNF-α. It mediates a large variety of inflammatory, immunostimulatory, and antiviral responses.
-

TNF-β, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsTNF is secreted by macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, T-cells, NK-cells following their stimulation by bacterial LPS. Cells expressing CD4 secrete TNF-alpha while CD8 cells secrete little or no TNF-alpha. The synthesis of TNF-alpha is induced by many different stimuli including interferons, IL2, GM-CSF. TNF-β is a potent mediator of inflammatory and immune responses. It belongs to the TNF family of ligands, and signals through TNFR1 and TNFR2. TNF-β is produced by activated T and B lymphocytes, and has similar activities to TNF-α. It mediates a large variety of inflammatory, immunostimulatory, and antiviral responses.
-
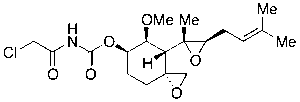
TNP-470
$220.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19H28ClNO6
-

TNP-470
$934.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19H28ClNO6
-

TNP-470
$1,451.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19H28ClNO6
-
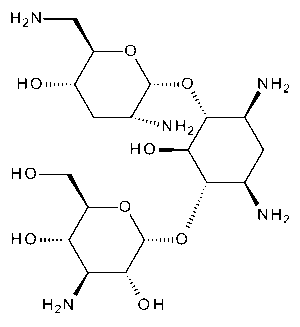
Tobramycin
$66.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H37 N5 O9
-

Tobramycin
$77.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H37 N5 O9
-

Tobramycin
$125.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H37 N5 O9
-

Tobramycin
$163.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsTobramycin
-

Tobramycin
$657.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsTobramycin
-
Tobramycin Deuterated
$251.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H37N5O9 for undeuterated
-
Tobramycin Deuterated
$1,911.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H37N5O9 for undeuterated
-
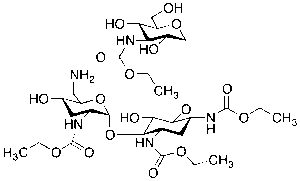
Tobramycin N’-Tetraethoxycarbonyl
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H53 N5 O17
-

Tobramycin N’-Tetraethoxycarbonyl
$357.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H53 N5 O17
-

Tobramycin N’-Tetraethoxycarbonyl
$687.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H53 N5 O17
-

Tobramycin Sulfate, USP
$283.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsTobramycin Sulfate, USP
-

Tobramycin Sulfate, USP
$629.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsTobramycin Sulfate, USP
-

Tobramycin Sulfate, USP
$907.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsTobramycin Sulfate, USP
-

Tobramycin Sulfate, USP
$3,686.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsTobramycin Sulfate, USP
-
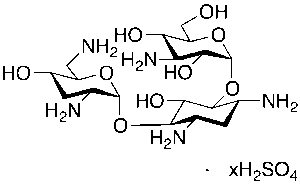
Tobramycin Sulphate Salt
$58.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H37N5O9 • x( H2O4S)
-

Tobramycin Sulphate Salt
$81.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H37N5O9 • x( H2O4S)
-

Tobramycin Sulphate Salt
$109.54 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H37N5O9 • x( H2O4S)
-

Tobramycin-D, 18O Acetic Acid Salt
$933.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H36DN5O8¹⁸O . (xCH3COOH)
-

Tobramycin-D, 18O Acetic Acid Salt
$1,781.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H36DN5O8¹⁸O . (xCH3COOH)
-

Tobramycin-D, 18O Acetic Acid Salt
$7,454.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H36DN5O8¹⁸O . (xCH3COOH)
-

Tocainide Hydrochloride
$130.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H16 N2 O . Cl H
-

Tocainide Hydrochloride
$508.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H16 N2 O . Cl H
-
Toceranib Phosphate
$62.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H25FN4O2 . H3PO4
-
Toceranib Phosphate
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H25FN4O2 . H3PO4
-

Tocofersolan
$77.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C33H54O5(C2H4O)n
-

Tocofersolan
$114.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C33H54O5(C2H4O)n
-

Tocofersolan
$228.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C33H54O5(C2H4O)n
-

Tocol
$53.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H44 O2
-

Tocol
$553.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H44 O2
-

TOCOPHEROL DEFICIENT DIET
$652.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsTOCOPHEROL DEFICIENT DIET
-

TOCOPHEROL DEFICIENT DIET
$1,144.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsTOCOPHEROL DEFICIENT DIET






