Ambient
Showing 144701–144750 of 146505 results
-

VEGF164, Rat (CHO-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor A164 (VEGF-A164), a member of the cysteine knot growth factor, is one of major isoforms of VEGF-As. VEGF-As are endothelial cell-specific mitogens with angiogenic and vascular permeability-inducing properties. During maturation, rat VEGF-A is alternatively spliced to generate rVEGF-A120, rVEGF-A164 and rVEGF-A188 which correspond to hVEGF-A121, hVEGF-A165 and hVEGF-A189 in human, respectively (the numbers designate the amino acid residues). The active form of rVEGF-A164 is either a homodimeric or heterodimeric polypeptides which bind to the transmembrane tyrosine kinases receptors FLT1, FLK1 or KDR or to the non-tyrosine kinase neuropilin receptors NRP1/2.
-

VEGF164, Rat (CHO-expressed)
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor A164 (VEGF-A164), a member of the cysteine knot growth factor, is one of major isoforms of VEGF-As. VEGF-As are endothelial cell-specific mitogens with angiogenic and vascular permeability-inducing properties. During maturation, rat VEGF-A is alternatively spliced to generate rVEGF-A120, rVEGF-A164 and rVEGF-A188 which correspond to hVEGF-A121, hVEGF-A165 and hVEGF-A189 in human, respectively (the numbers designate the amino acid residues). The active form of rVEGF-A164 is either a homodimeric or heterodimeric polypeptides which bind to the transmembrane tyrosine kinases receptors FLT1, FLK1 or KDR or to the non-tyrosine kinase neuropilin receptors NRP1/2.
-

VEGF165, Human
$1,470.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) is a potent growth and angiogenic cytokine. It stimulates proliferation and survival of endothelial cells, and promotes angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Expressed in vascularized tissues, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) plays a prominent role in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Substantial evidence implicates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in the induction of tumor metastasis and intra-ocular neovascular syndromes. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) signals through the three receptors; fms-like tyrosine kinase (flt-1), KDR gene product (the murine homolog of KDR is the flk-1 gene product) and the flt4 gene product.
-

VEGF165, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) is a potent growth and angiogenic cytokine. It stimulates proliferation and survival of endothelial cells, and promotes angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Expressed in vascularized tissues, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) plays a prominent role in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Substantial evidence implicates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in the induction of tumor metastasis and intra-ocular neovascular syndromes. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) signals through the three receptors; fms-like tyrosine kinase (flt-1), KDR gene product (the murine homolog of KDR is the flk-1 gene product) and the flt4 gene product.
-

VEGF165, Human
$392.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) is a potent growth and angiogenic cytokine. It stimulates proliferation and survival of endothelial cells, and promotes angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Expressed in vascularized tissues, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) plays a prominent role in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Substantial evidence implicates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in the induction of tumor metastasis and intra-ocular neovascular syndromes. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) signals through the three receptors; fms-like tyrosine kinase (flt-1), KDR gene product (the murine homolog of KDR is the flk-1 gene product) and the flt4 gene product.
-

VEGF165, Human
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) is a potent growth and angiogenic cytokine. It stimulates proliferation and survival of endothelial cells, and promotes angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Expressed in vascularized tissues, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) plays a prominent role in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Substantial evidence implicates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in the induction of tumor metastasis and intra-ocular neovascular syndromes. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) signals through the three receptors; fms-like tyrosine kinase (flt-1), KDR gene product (the murine homolog of KDR is the flk-1 gene product) and the flt4 gene product.
-

VEGF165, Human(HEK 293-expressed)
$1,470.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) is a potent growth and angiogenic cytokine. It stimulates proliferation and survival of endothelial cells, and promotes angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Expressed in vascularized tissues, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) plays a prominent role in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Substantial evidence implicates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in the induction of tumor metastasis and intra-ocular neovascular syndromes. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) signals through the three receptors; fms-like tyrosine kinase (flt-1), KDR gene product (the murine homolog of KDR is the flk-1 gene product) and the flt4 gene product.
-

VEGF165, Human(HEK 293-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) is a potent growth and angiogenic cytokine. It stimulates proliferation and survival of endothelial cells, and promotes angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Expressed in vascularized tissues, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) plays a prominent role in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Substantial evidence implicates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in the induction of tumor metastasis and intra-ocular neovascular syndromes. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) signals through the three receptors; fms-like tyrosine kinase (flt-1), KDR gene product (the murine homolog of KDR is the flk-1 gene product) and the flt4 gene product.
-

VEGF165, Human(HEK 293-expressed)
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) is a potent growth and angiogenic cytokine. It stimulates proliferation and survival of endothelial cells, and promotes angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Expressed in vascularized tissues, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) plays a prominent role in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Substantial evidence implicates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in the induction of tumor metastasis and intra-ocular neovascular syndromes. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) signals through the three receptors; fms-like tyrosine kinase (flt-1), KDR gene product (the murine homolog of KDR is the flk-1 gene product) and the flt4 gene product.
-
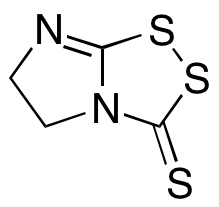
Vegita
$91.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H4 N2 S3
-

Vegita
$374.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H4 N2 S3
-

Vegita
$683.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H4 N2 S3
-
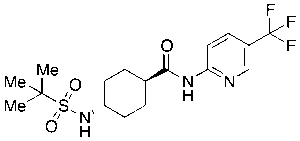
Velneprit
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H24F3N3O3S
-

Velneprit
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H24F3N3O3S
-
Velpatasvir
$65.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C49H54N8O8
-
Velpatasvir
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C49H54N8O8
-
Velpatasvir
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C49H54N8O8
-
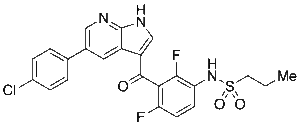
Vemurafenib
$61.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H18 Cl F2 N3 O3 S
-

Vemurafenib
$83.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H18 Cl F2 N3 O3 S
-

Vemurafenib
$172.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H18 Cl F2 N3 O3 S
-
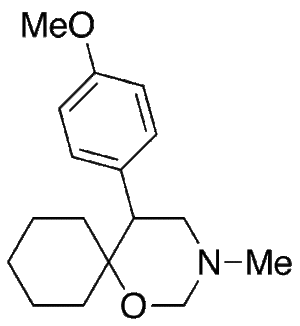
Venlafaxine Cyclic Impurity
$210.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H25 N O2
-

Venlafaxine Cyclic Impurity
$1,606.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H25 N O2
-
Venlafaxine N-Oxide
$223.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H27 N O3
-
Venlafaxine N-Oxide
$953.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H27 N O3
-
Venlafaxine N-Oxide
$1,798.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H27 N O3
-

Venlafaxine-d6 N-Oxide
$226.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H21D6NO3
-

Venlafaxine-d6 N-Oxide
$997.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H21D6NO3
-

Venlafaxine-d6 N-Oxide
$1,710.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H21D6NO3
-
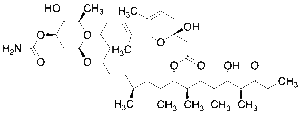
Venturicidin A
$732.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C41H67NO11
-

Veraguensin
$100.91 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H28O5
-

Veraguensin
$199.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H28O5
-

Veralipride
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H25N3O5S
-

Veralipride
$1,306.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H25N3O5S
-

Verapamil Ethyl Methanethiosulfonate, Bromide
$119.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H45 N2 O6 S2 . Br
-

Verapamil Ethyl Methanethiosulfonate, Bromide
$374.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H45 N2 O6 S2 . Br
-

Verapamil Ethyl Methanethiosulfonate, Bromide
$785.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H45 N2 O6 S2 . Br
-
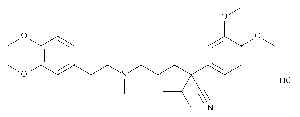
Verapamil Hydrochloride
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H38 N2 O4 . Cl H
-

Verapamil Hydrochloride
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H38 N2 O4 . Cl H
-

Verapamil Hydrochloride
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H38 N2 O4 . Cl H
-
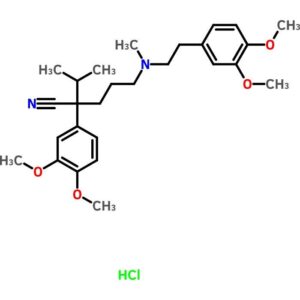
Verapamil Hydrochloride
$75.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsVerapamil Hydrochloride
-

Verapamil Hydrochloride
$251.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsVerapamil Hydrochloride
-

Verapamil Hydrochloride, USP
$110.02 Add to cart View Product DetailsVerapamil Hydrochloride, USP
-

Verapamil Hydrochloride, USP
$289.29 Add to cart View Product DetailsVerapamil Hydrochloride, USP
-

Verapamil Hydrochloride, USP
$962.54 Add to cart View Product DetailsVerapamil Hydrochloride, USP
-

Verapamil Hydrochloride, USP
$2,399.07 Add to cart View Product DetailsVerapamil Hydrochloride, USP
-

Verapamil Hydrochloride, USP
$4,812.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsVerapamil Hydrochloride, USP
-

Verapamil Hydrochloride, USP
$10,841.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsVerapamil Hydrochloride, USP
-

Verapamil-d3 Hydrochloride
$323.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 D3 H35 N2 O4 . Cl H
-

Verapamil-d3 Hydrochloride
$1,467.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 D3 H35 N2 O4 . Cl H
-

Verapamil-d6
$288.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 D6 H32 N2 O4






