Shop
Showing 157601–157650 of 278485 results
-

IL-7, His, Mouse
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-7 (IL-7), also known as lymphopoietin 1 and pre-B cell factor, is a hematopoietic growth factor belonging to the IL-7/IL-9 family. It is produced by keratinocytes, dendritic cells, hepatocytes, neurons and epithelial cells. IL-7 binds and signals through IL-7 receptor, a heterodimer consisting of IL-7 receptor alpha and common gamma chain receptor. IL-7 plays a role in regulating early B cell and T cell development. It is also important for optimal dendritic cell-T cell interaction.
-

IL-7, His, Mouse
$314.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-7 (IL-7), also known as lymphopoietin 1 and pre-B cell factor, is a hematopoietic growth factor belonging to the IL-7/IL-9 family. It is produced by keratinocytes, dendritic cells, hepatocytes, neurons and epithelial cells. IL-7 binds and signals through IL-7 receptor, a heterodimer consisting of IL-7 receptor alpha and common gamma chain receptor. IL-7 plays a role in regulating early B cell and T cell development. It is also important for optimal dendritic cell-T cell interaction.
-

IL-7, Human
$3,458.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-7 (IL-7), also known as lymphopoietin 1 and pre-B cell factor, is a hematopoietic growth factor belonging to the IL-7/IL-9 family. It is produced by keratinocytes, dendritic cells, hepatocytes, neurons and epithelial cells. IL-7 binds and signals through IL-7 receptor, a heterodimer consisting of IL-7 receptor alpha and common gamma chain receptor. IL-7 plays a role in regulating early B cell and T cell development. It is also important for optimal dendritic cell-T cell interaction.
-

IL-7, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-7 (IL-7), also known as lymphopoietin 1 and pre-B cell factor, is a hematopoietic growth factor belonging to the IL-7/IL-9 family. It is produced by keratinocytes, dendritic cells, hepatocytes, neurons and epithelial cells. IL-7 binds and signals through IL-7 receptor, a heterodimer consisting of IL-7 receptor alpha and common gamma chain receptor. IL-7 plays a role in regulating early B cell and T cell development. It is also important for optimal dendritic cell-T cell interaction.
-
IL-8 (77aa)/CXCL8, Human
$1,323.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-8 (IL-8), also known as CXCL8, GCP-1 and NAP-1, is one of the first discovered chemokines and belongs to the CXCL family, in which the first two conserved cysteines are separated by one residue. In vivo, IL-8 exists in two forms: a 77 a.a. protein produced by endothelial cells, and the more active 72 a.a. protein produced by monocytes. The receptors for IL-8 are the seven-helical G-protein coupled receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2, exclusively expressed on neutrophils. The functions of IL-8 are to induce rapid changes in cell morphology, activate integrins, and release the granule contents of neutrophils. Thus, IL-8 can enhance the antimicrobial actions of defense cells. It is secreted by monocytes, macrophages and endothelial cells. IL-8 signals through CXCR1 and CXCR2 to chemoattract neutrophils, basophils, and T cells. IL-8 is also a potent promoter of angiogenesis. Other functions of this protein, such as involvement in bronchiolitis pathogenesis, have also been reported.
-

IL-8 (77aa)/CXCL8, Human
$90.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-8 (IL-8), also known as CXCL8, GCP-1 and NAP-1, is one of the first discovered chemokines and belongs to the CXCL family, in which the first two conserved cysteines are separated by one residue. In vivo, IL-8 exists in two forms: a 77 a.a. protein produced by endothelial cells, and the more active 72 a.a. protein produced by monocytes. The receptors for IL-8 are the seven-helical G-protein coupled receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2, exclusively expressed on neutrophils. The functions of IL-8 are to induce rapid changes in cell morphology, activate integrins, and release the granule contents of neutrophils. Thus, IL-8 can enhance the antimicrobial actions of defense cells. It is secreted by monocytes, macrophages and endothelial cells. IL-8 signals through CXCR1 and CXCR2 to chemoattract neutrophils, basophils, and T cells. IL-8 is also a potent promoter of angiogenesis. Other functions of this protein, such as involvement in bronchiolitis pathogenesis, have also been reported.
-

IL-8 (77aa)/CXCL8, Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-8 (IL-8), also known as CXCL8, GCP-1 and NAP-1, is one of the first discovered chemokines and belongs to the CXCL family, in which the first two conserved cysteines are separated by one residue. In vivo, IL-8 exists in two forms: a 77 a.a. protein produced by endothelial cells, and the more active 72 a.a. protein produced by monocytes. The receptors for IL-8 are the seven-helical G-protein coupled receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2, exclusively expressed on neutrophils. The functions of IL-8 are to induce rapid changes in cell morphology, activate integrins, and release the granule contents of neutrophils. Thus, IL-8 can enhance the antimicrobial actions of defense cells. It is secreted by monocytes, macrophages and endothelial cells. IL-8 signals through CXCR1 and CXCR2 to chemoattract neutrophils, basophils, and T cells. IL-8 is also a potent promoter of angiogenesis. Other functions of this protein, such as involvement in bronchiolitis pathogenesis, have also been reported.
-

IL-8/CXCL8 (77aa), Human(CHO-expressed)
$1,177.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-8 (IL-8), also known as CXCL8, GCP-1 and NAP-1, is one of the first discovered chemokines and belongs to the CXCL family, in which the first two conserved cysteines are separated by one residue. In vivo, IL-8 exists in two forms: a 77 a.a. protein produced by endothelial cells, and the more active 72 a.a. protein produced by monocytes. The receptors for IL-8 are the seven-helical G-protein coupled receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2, exclusively expressed on neutrophils. The functions of IL-8 are to induce rapid changes in cell morphology, activate integrins, and release the granule contents of neutrophils. Thus, IL-8 can enhance the antimicrobial actions of defense cells. It is secreted by monocytes, macrophages and endothelial cells. IL-8 signals through CXCR1 and CXCR2 to chemoattract neutrophils, basophils, and T cells. IL-8 is also a potent promoter of angiogenesis. Other functions of this protein, such as involvement in bronchiolitis pathogenesis, have also been reported.
-

IL-8/CXCL8 (77aa), Human(CHO-expressed)
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-8 (IL-8), also known as CXCL8, GCP-1 and NAP-1, is one of the first discovered chemokines and belongs to the CXCL family, in which the first two conserved cysteines are separated by one residue. In vivo, IL-8 exists in two forms: a 77 a.a. protein produced by endothelial cells, and the more active 72 a.a. protein produced by monocytes. The receptors for IL-8 are the seven-helical G-protein coupled receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2, exclusively expressed on neutrophils. The functions of IL-8 are to induce rapid changes in cell morphology, activate integrins, and release the granule contents of neutrophils. Thus, IL-8 can enhance the antimicrobial actions of defense cells. It is secreted by monocytes, macrophages and endothelial cells. IL-8 signals through CXCR1 and CXCR2 to chemoattract neutrophils, basophils, and T cells. IL-8 is also a potent promoter of angiogenesis. Other functions of this protein, such as involvement in bronchiolitis pathogenesis, have also been reported.
-

IL-8/CXCL8 (77aa), Human(CHO-expressed)
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-8 (IL-8), also known as CXCL8, GCP-1 and NAP-1, is one of the first discovered chemokines and belongs to the CXCL family, in which the first two conserved cysteines are separated by one residue. In vivo, IL-8 exists in two forms: a 77 a.a. protein produced by endothelial cells, and the more active 72 a.a. protein produced by monocytes. The receptors for IL-8 are the seven-helical G-protein coupled receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2, exclusively expressed on neutrophils. The functions of IL-8 are to induce rapid changes in cell morphology, activate integrins, and release the granule contents of neutrophils. Thus, IL-8 can enhance the antimicrobial actions of defense cells. It is secreted by monocytes, macrophages and endothelial cells. IL-8 signals through CXCR1 and CXCR2 to chemoattract neutrophils, basophils, and T cells. IL-8 is also a potent promoter of angiogenesis. Other functions of this protein, such as involvement in bronchiolitis pathogenesis, have also been reported.
-
IL-9, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin 9, also known as IL9, is a cytokine (cell signalling molecule) belonging to the group of interleukins. The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine produced by T-cells and specifically by CD4+ helper cells that acts as a regulator of a variety of hematopoietic cells. This cytokine stimulates cell proliferation and prevents apoptosis. It functions through the interleukin-9 receptor (IL9R), which activates different signal transducer and activator (STAT) proteins and thus connects this cytokine to various biological processes. The gene encoding this cytokine has been identified as a candidate gene for asthma. Genetic studies on a mouse model of asthma demonstrated that this cytokine is a determining factor in the pathogenesis of bronchial hyperresponsiveness.
-

IL-9, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin 9, also known as IL9, is a cytokine (cell signalling molecule) belonging to the group of interleukins. The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine produced by T-cells and specifically by CD4+ helper cells that acts as a regulator of a variety of hematopoietic cells. This cytokine stimulates cell proliferation and prevents apoptosis. It functions through the interleukin-9 receptor (IL9R), which activates different signal transducer and activator (STAT) proteins and thus connects this cytokine to various biological processes. The gene encoding this cytokine has been identified as a candidate gene for asthma. Genetic studies on a mouse model of asthma demonstrated that this cytokine is a determining factor in the pathogenesis of bronchial hyperresponsiveness.
-

IL-9, Human
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin 9, also known as IL9, is a cytokine (cell signalling molecule) belonging to the group of interleukins. The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine produced by T-cells and specifically by CD4+ helper cells that acts as a regulator of a variety of hematopoietic cells. This cytokine stimulates cell proliferation and prevents apoptosis. It functions through the interleukin-9 receptor (IL9R), which activates different signal transducer and activator (STAT) proteins and thus connects this cytokine to various biological processes. The gene encoding this cytokine has been identified as a candidate gene for asthma. Genetic studies on a mouse model of asthma demonstrated that this cytokine is a determining factor in the pathogenesis of bronchial hyperresponsiveness.
-

IL-9, Mouse
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin 9, also known as IL9, is a cytokine (cell signalling molecule) belonging to the group of interleukins. The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine produced by T-cells and specifically by CD4+ helper cells that acts as a regulator of a variety of hematopoietic cells. This cytokine stimulates cell proliferation and prevents apoptosis. It functions through the interleukin-9 receptor (IL9R), which activates different signal transducer and activator (STAT) proteins and thus connects this cytokine to various biological processes. The gene encoding this cytokine has been identified as a candidate gene for asthma. Genetic studies on a mouse model of asthma demonstrated that this cytokine is a determining factor in the pathogenesis of bronchial hyperresponsiveness.
-

IL-9, Mouse
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin 9, also known as IL9, is a cytokine (cell signalling molecule) belonging to the group of interleukins. The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine produced by T-cells and specifically by CD4+ helper cells that acts as a regulator of a variety of hematopoietic cells. This cytokine stimulates cell proliferation and prevents apoptosis. It functions through the interleukin-9 receptor (IL9R), which activates different signal transducer and activator (STAT) proteins and thus connects this cytokine to various biological processes. The gene encoding this cytokine has been identified as a candidate gene for asthma. Genetic studies on a mouse model of asthma demonstrated that this cytokine is a determining factor in the pathogenesis of bronchial hyperresponsiveness.
-

IL-9, Mouse
$340.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin 9, also known as IL9, is a cytokine (cell signalling molecule) belonging to the group of interleukins. The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine produced by T-cells and specifically by CD4+ helper cells that acts as a regulator of a variety of hematopoietic cells. This cytokine stimulates cell proliferation and prevents apoptosis. It functions through the interleukin-9 receptor (IL9R), which activates different signal transducer and activator (STAT) proteins and thus connects this cytokine to various biological processes. The gene encoding this cytokine has been identified as a candidate gene for asthma. Genetic studies on a mouse model of asthma demonstrated that this cytokine is a determining factor in the pathogenesis of bronchial hyperresponsiveness.
-

IL10 Rabbit mAb
$296.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

IL10 Rabbit mAb
$119.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-
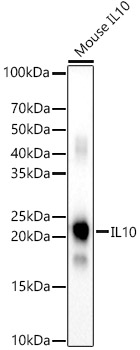
IL10 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL10 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL10 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL10 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL11RA Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

IL11RA Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-
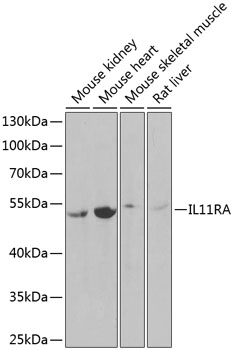
IL11RA Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL11RA Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
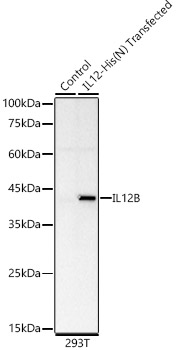
IL12 Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

IL12 Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

IL12 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL12 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL12A Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL12A Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL12B Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

IL12B Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

IL12B Rabbit mAb
$296.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

IL12B Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-
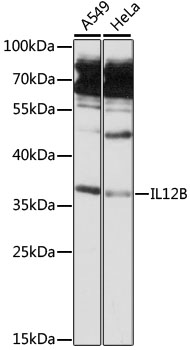
IL12B Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
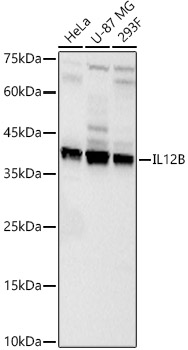
IL12B Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL12B Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL12B Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
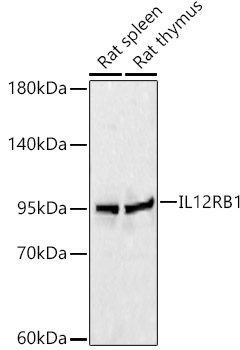
IL12RB1 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL12RB1 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
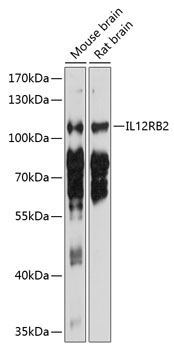
IL12RB2 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL12RB2 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL13 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
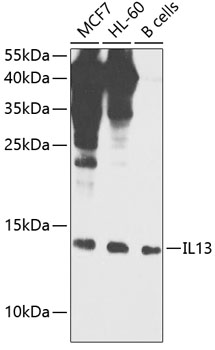
IL13 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL13 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL13 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IL13RA1 Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

IL13RA1 Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies






