1
Showing 53701–53750 of 57739 results
-

VapLock Solvent Waste Kit, PP, 70 mm Rieke 6TPI, 1×1/2 in. NPT, 3×1/4 in. NPT, 6×1/4-28 UNF
$367.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsVapLock Solvent Waste Kit, PP, 70 mm Rieke 6TPI, 1×1/2 in. NPT, 3×1/4 in. NPT, 6×1/4-28 UNF
-

VapLock Tubing Adapter, 1/16 in. OD x 1/4 NPT(M), Green PP Fitting, Blue ETFE Ferrule, PP Body
$16.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsVapLock Tubing Adapter, 1/16 in. OD x 1/4 NPT(M), Green PP Fitting, Blue ETFE Ferrule, PP Body
-

VapLock Tubing Adapter, 4 mm OD x 5/16-24 UNF(M), Brown PEEK Fitting, White PCTFE Ferrule
$13.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsVapLock Tubing Adapter, 4 mm OD x 5/16-24 UNF(M), Brown PEEK Fitting, White PCTFE Ferrule
-

Vapreotide
$240.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsVapreotide
-

Vardenafil Dimer
$87.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C38 H46 N10 O8 S2
-

Vardenafil-d5
$210.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 2H5 H27 N6 O4 S
-
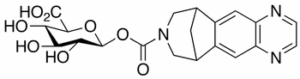
Varenicline Carbamoyl Beta-D-Glucuronide
$219.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H21N3O8
-
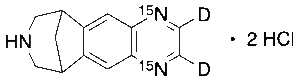
Varenicline-d2,15N2 Dihydrochloride
$274.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H13D2Cl2N15N2
-

Variable Height Mobile Bench
$2,461.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsVariable Height Mobile Bench
-

Variable Speed Mini Orbitron Nutating Mixer 4-24 RPM 115V/230V
$465.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsVariable Speed Mini Orbitron Nutating Mixer 4-24 RPM 115V/230V
-

Variable Speed Tube Revolver with Digital Display, 10-40 RPM
$538.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsVariable Speed Tube Revolver with Digital Display, 10-40 RPM
-

Variable Speed Tube Revolver, 10-40 rpm, 100-240V, 50/60Hz
$565.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsVariable Speed Tube Revolver, 10-40 rpm, 100-240V, 50/60Hz
-

Variable Speed Vortexing Mixer 110/120V, US Plug
$312.17 Add to cart View Product DetailsVariable Speed Vortexing Mixer 110/120V, US Plug
-

Variable Speed Vortexing Mixer 230/40 CE Plug
$312.17 Add to cart View Product DetailsVariable Speed Vortexing Mixer 230/40 CE Plug
-

Vatalanib-d4 Dihydrochloride
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H13D4Cl3N4
-
VDRL BENT Needle 1/PK (18/-/3)
$11.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsVDRL BENT Needle 1/PK (18/-/3)
-

VE-300PAD Digital Microscope With Integrated Tablet
$5,331.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-300PAD Digital Microscope With Integrated Tablet
-

VE-41 Trinocular Inverted Microscope
$7,109.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-41 Trinocular Inverted Microscope
-

VE-8000A UV and Visible Light Spectrophotometer w/ Double Littrow Beam
$12,116.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-8000A UV and Visible Light Spectrophotometer w/ Double Littrow Beam
-

VE-A50 Binocular Microscope
$964.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-A50 Binocular Microscope
-

VE-B2 Plus Plan Binocular Microscope
$1,092.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-B2 Plus Plan Binocular Microscope
-

VE-B400 Biological Microscope
$3,194.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-B400 Biological Microscope
-
VE-BC3 PLUS Binocular Microscope with Integrated 3.0 MP Digital Camera
$1,685.90 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-BC3 PLUS Binocular Microscope with Integrated 3.0 MP Digital Camera
-

VE-BC3 PLUS PLAN Binocular Microscope with Integrated 3.0 MP Digital Camera
$1,693.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-BC3 PLUS PLAN Binocular Microscope with Integrated 3.0 MP Digital Camera
-

VE-BC3 PLUS PLAN(IN) Binocular Microscope with Integrated 5.0 MP Digital Camera
$2,160.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-BC3 PLUS PLAN(IN) Binocular Microscope with Integrated 5.0 MP Digital Camera
-

VE-CS15S Counting Scale 15 kg/30 lb 0.5 g/0.001 lb
$238.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-CS15S Counting Scale 15 kg/30 lb 0.5 g/0.001 lb
-

VE-CS30S Counting Scale 30 kg/60 lb 1 g/0.002 lb
$238.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-CS30S Counting Scale 30 kg/60 lb 1 g/0.002 lb
-

VE-CS6S Counting Scale 6 kg /12 lb 0.2 g/0.0005 lb
$238.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-CS6S Counting Scale 6 kg /12 lb 0.2 g/0.0005 lb
-
VE-D50 Digital Microscope
$1,889.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-D50 Digital Microscope
-

VE-LX1000 10.0 MP Digital Camera for Microscopes
$790.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-LX1000 10.0 MP Digital Camera for Microscopes
-

VE-LX1400 14.0 Digital Camera for Microscopes
$885.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-LX1400 14.0 Digital Camera for Microscopes
-

VE-M5DTH Dual View Compound Microscope
$598.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-M5DTH Dual View Compound Microscope
-
VE-S7 Binocular Stereoscope
$1,273.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-S7 Binocular Stereoscope
-

VE-SLIDES Microscope Slides
$10.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-SLIDES Microscope Slides
-

VE-T50 Trinocular Microscope
$1,366.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsVE-T50 Trinocular Microscope
-
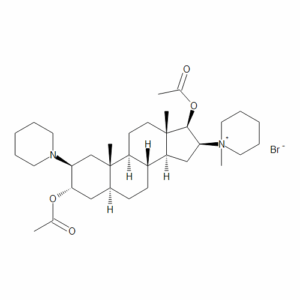
Vecuronium Bromide
$1,763.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H57 N2 O4 . Br
-
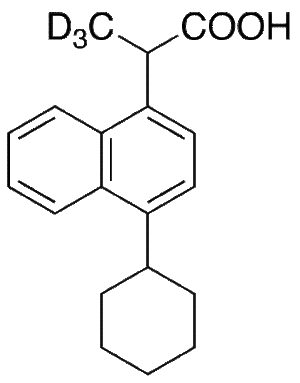
Vedaprofen-d3
$210.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19H19D3O2
-

Vedaprofen, NeuroPure
$235.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsVedaprofen, NeuroPure
-

Vee Gee Microscope Immersion Oil, Low Viscosity, 1/4 oz
$13.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsVee Gee Microscope Immersion Oil, Low Viscosity, 1/4 oz
-

Vee Gee Microscope Objective, 40x Achromatic (DIN)/0.65 N.A.
$79.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsVee Gee Microscope Objective, 40x Achromatic (DIN)/0.65 N.A.
-
Vee Gee Scientific API ASTM 54H Hydrometers with SafetyBLUE F Thermometer, 29 to 41 API
$55.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsVee Gee Scientific API ASTM 54H Hydrometers with SafetyBLUE F Thermometer, 29 to 41 API
-

Vee Gee Scientific Microscope Fuse, 0.75A / 250V, for 1250s, 1260s, 1270ZFs, 1270ZHs, 1130s
$2.02 Add to cart View Product DetailsVee Gee Scientific Microscope Fuse, 0.75A / 250V, for 1250s, 1260s, 1270ZFs, 1270ZHs, 1130s
-

Vee Gee Scientific Microscope Fuse, 1270ZLs, 1250SLs, 1130ZLs, Newer 1490s
$2.02 Add to cart View Product DetailsVee Gee Scientific Microscope Fuse, 1270ZLs, 1250SLs, 1130ZLs, Newer 1490s
-

Vee Gee Scientific Microscope Fuse, 5.0A / 250V, for 1282ECM and 1286ECM External Power Supply
$2.02 Add to cart View Product DetailsVee Gee Scientific Microscope Fuse, 5.0A / 250V, for 1282ECM and 1286ECM External Power Supply
-

VEGETABLE OIL HYDROGENATED
$45.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsVEGETABLE OIL HYDROGENATED
-
VEGF-A164, Mouse
$1,470.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) was initially purified from media conditioned by normal bovine pituitary folliculo-stellate cells and by a variety of transformed cell lines as a mitogen specific for vascular endothelial cells. It was subsequently found to be identical to an independently discovered vascular permeability factor (VPF), which was previously identified in media conditioned by tumor cell lines based on its ability to increase the permeability of capillary blood vessels. Three mouse cDNA clones, which arise through alternative splicing and which encode mature mouse monomeric VEGF having 120, 164, or 188, amino acids, respectively, have been identified. Two receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), Flt-1 and Flk-1 (the mouse homologue of human KDR), both members of the type III subclass of RTKs containing seven immunoglobulin-like repeats in their extracellular domains, have been shown to bind VEGF with high affinity. The roles of the homodimers of KDR, Flt, and the heterodimer of KDR/Flt in VEGF signal transduction remain to be elucidated. In vivo, VEGF has been found to be a potent angiogenesis inducer.
-

VEGF-C, Human
$1,323.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor (PDGF/VEGF) family, is active in angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and endothelial cell growth and survival, and can also affect the permeability of blood vessels. VEGF-C is expressed in various tissues, however it is not produced in peripheral blood lymphocytes. It forms cell surface-associated non-covalent disulfide linked homodimers, and can bind and activate both VEGFR-2 (flk1) and VEGFR-3 (flt4) receptors. The structure and function of VEGF-C is similar to those of vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D).
-

VEGF-D, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)-D, also known as c-Fos-induced growth factor (FIGF), is a member of the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family. It is expressed highly in lung, heart and small intestine, and at lower levels in skeletal muscle, colon and pancreas. It binds to VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 receptors and activates downstream signals. VEGF-D is a growth factor active in angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and endothelial cell growth. It is involved in many developmental and physiological processes including the formation of venous and lymphatic vascular systems during embryogenesis and the maintenance of differentiated lymphatic endothelium in adults. In tumor pathology, it has been reported to play a role in restructuring of lymphatic channels and regional lymph node metastasis.
-

VEGF-R2 Fc Chimera, Mouse
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsVEGF-R2 belongs to a family of proteins called receptor tyrosine kinases. The receptor has three main parts: one part extends out of the cell and binds to VEGF, another spans the cell’s membrane, while the third part is found inside the cell. The current model of VEGF-R2 activation is that VEGF binds to individual VEGF-R2 receptor proteins on the membrane, and brings two of them close enough to form a complex called a dimer. The receptor dimer is activated and initiates signaling within the cell. VEGF-R2 is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) which transduces biochemical signals via lateral dimerization in the plasma membrane. Like most RTKs, VEGF-R2 is composed of an extracellular (EC) domain, a transmembrane (TM) domain, and an intracellular (IC) domain consisting of a kinase domain and sequences required for downstream signaling. The EC domain consists of seven immunoglobulin homology (Ig) domains, termed D1 (at the N-terminus) to D7 (closest to the membrane). VEGF-R2 binds to, and is activated by the ligands VEGF-A, VEGF-E, and a number of processed forms of VEGF-C and VEGF-D. Ligand binding to VEGF-R2 is mediated by Ig-domains 2 and 3 and the linker between D2 and D3.
-

VEGF120, Mouse
$3,187.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsVEGF was initially purified from media conditioned by normal bovine pituitary folliculo-stellate cells and by a variety of transformed cell lines as a mitogen specific for vascular endothelial cells. It was subsequently found to be identical to an independently discovered vascular permeability factor (VPF), which was previously identified in media conditioned by tumor cell lines based on its ability to increase the permeability of capillary blood vessels. Three mouse cDNA clones, which arise through alternative splicing and which encode mature mouse monomeric VEGF having 120, 164, or 188, amino acids, respectively, have been identified. Two receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), Flt-1 and Flk-1 (the mouse homologue of human KDR), both members of the type III subclass of RTKs containing seven immunoglobulin-like repeats in their extracellular domains, have been shown to bind VEGF with high affinity. The roles of the homodimers of KDR, Flt, and the heterodimer ofKDR/Flt in VEGF signal transduction remain to be elucidated.In vivo, VEGF has been found to be a potent angiogenesis inducer.






