10
Showing 25951–26000 of 26336 results
-
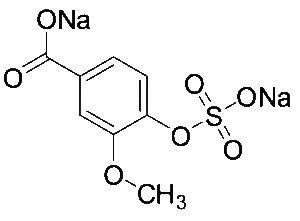
Vanillic Acid 4-Sulphate Sodium Salt
$165.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H6 Na2 O7 S
-
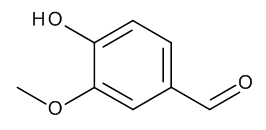
Vanillin
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H8 O3
-

Vanillin-13C6
$2,495.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C6 C2 H8 O3
-

Vanillyl Methyl Ketone-d5
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H7D5O3
-
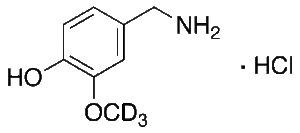
Vanillylamine-d3 Hydrochloride
$1,022.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H9D3ClNO2
-

VapLock Port Plug, 1/4 in. NPT(M), Polypropylene
$11.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsVapLock Port Plug, 1/4 in. NPT(M), Polypropylene
-

VapLock Port Plug, 3/8 in. NPT(M), Polypropylene
$10.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsVapLock Port Plug, 3/8 in. NPT(M), Polypropylene
-
VapLock Tubing Adapter, 1/2 in. ID x 1/4 in. NPT(M), Polypropylene
$9.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsVapLock Tubing Adapter, 1/2 in. ID x 1/4 in. NPT(M), Polypropylene
-

VapLock Tubing Adapter, 1/4 in. ID x 1/4 in. NPT(M), Polypropylene
$8.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsVapLock Tubing Adapter, 1/4 in. ID x 1/4 in. NPT(M), Polypropylene
-

VapLock Tubing Adapter, 1/4 in. ID x 1/8 in. NPT(M), Polypropylene
$8.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsVapLock Tubing Adapter, 1/4 in. ID x 1/8 in. NPT(M), Polypropylene
-

VapLock Tubing Adapter, 1/8 in. OD x 1/4-28 UNF(M), Blue PP Fitting, Yellow ETFE Ferrule, Pack of 10
$46.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsVapLock Tubing Adapter, 1/8 in. OD x 1/4-28 UNF(M), Blue PP Fitting, Yellow ETFE Ferrule, Pack of 10
-

Vardenafil Dihydrochloride Salt
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H32 N6 O4 S . 2 Cl H
-

Vardenafil Dimer
$415.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C38 H46 N10 O8 S2
-
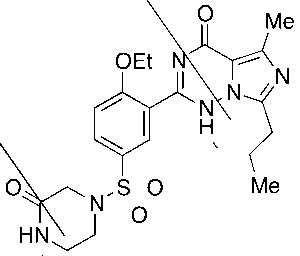
Vardenafil Oxopiperazine (Impurity)
$211.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 H26 N6 O5 S
-

Vardenafil Oxopiperazine-D6 (Impurity)
$512.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 D6 H20 N6 O5 S
-

Vardenafil-d5
$1,554.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 2H5 H27 N6 O4 S
-

Varenicline
$423.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H13 N3
-

Varenicline N-Glucoside
$724.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H23 N3 O5
-
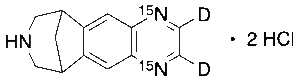
Varenicline-d2,15N2 Dihydrochloride
$2,126.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H13D2Cl2N15N2
-

Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-165
$756.27 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor-165
-

Vasopressin Acetic Acid Salt
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C46H65N15O12S2 • (C2H4O2)
-

Vatalanib Dihydrochloride
$69.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H15 Cl N4 . 2 Cl H
-
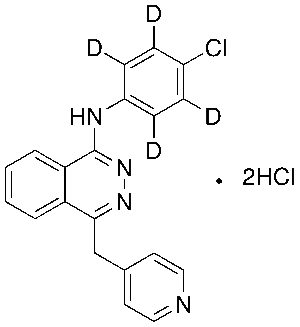
Vatalanib-d4 Dihydrochloride
$1,296.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H13D4Cl3N4
-
VE 821
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H16N4O3S
-

Vecuronium Bromide
$77.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H57 N2 O4 . Br
-

Vedaprofen
$236.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H22 O2
-

Vedaprofen-d3
$1,589.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19H19D3O2
-
VEGF-A164, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) was initially purified from media conditioned by normal bovine pituitary folliculo-stellate cells and by a variety of transformed cell lines as a mitogen specific for vascular endothelial cells. It was subsequently found to be identical to an independently discovered vascular permeability factor (VPF), which was previously identified in media conditioned by tumor cell lines based on its ability to increase the permeability of capillary blood vessels. Three mouse cDNA clones, which arise through alternative splicing and which encode mature mouse monomeric VEGF having 120, 164, or 188, amino acids, respectively, have been identified. Two receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), Flt-1 and Flk-1 (the mouse homologue of human KDR), both members of the type III subclass of RTKs containing seven immunoglobulin-like repeats in their extracellular domains, have been shown to bind VEGF with high affinity. The roles of the homodimers of KDR, Flt, and the heterodimer of KDR/Flt in VEGF signal transduction remain to be elucidated. In vivo, VEGF has been found to be a potent angiogenesis inducer.
-

VEGF-C, Human
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor (PDGF/VEGF) family, is active in angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and endothelial cell growth and survival, and can also affect the permeability of blood vessels. VEGF-C is expressed in various tissues, however it is not produced in peripheral blood lymphocytes. It forms cell surface-associated non-covalent disulfide linked homodimers, and can bind and activate both VEGFR-2 (flk1) and VEGFR-3 (flt4) receptors. The structure and function of VEGF-C is similar to those of vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D).
-

VEGF-D, Human
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)-D, also known as c-Fos-induced growth factor (FIGF), is a member of the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family. It is expressed highly in lung, heart and small intestine, and at lower levels in skeletal muscle, colon and pancreas. It binds to VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 receptors and activates downstream signals. VEGF-D is a growth factor active in angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and endothelial cell growth. It is involved in many developmental and physiological processes including the formation of venous and lymphatic vascular systems during embryogenesis and the maintenance of differentiated lymphatic endothelium in adults. In tumor pathology, it has been reported to play a role in restructuring of lymphatic channels and regional lymph node metastasis.
-

VEGF120, Mouse
$194.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsVEGF was initially purified from media conditioned by normal bovine pituitary folliculo-stellate cells and by a variety of transformed cell lines as a mitogen specific for vascular endothelial cells. It was subsequently found to be identical to an independently discovered vascular permeability factor (VPF), which was previously identified in media conditioned by tumor cell lines based on its ability to increase the permeability of capillary blood vessels. Three mouse cDNA clones, which arise through alternative splicing and which encode mature mouse monomeric VEGF having 120, 164, or 188, amino acids, respectively, have been identified. Two receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), Flt-1 and Flk-1 (the mouse homologue of human KDR), both members of the type III subclass of RTKs containing seven immunoglobulin-like repeats in their extracellular domains, have been shown to bind VEGF with high affinity. The roles of the homodimers of KDR, Flt, and the heterodimer ofKDR/Flt in VEGF signal transduction remain to be elucidated.In vivo, VEGF has been found to be a potent angiogenesis inducer.
-

VEGF121, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsVEGF-A121 is one of five isoforms (121, 145, 165, 189, and 206) of VEGF protein, a cytokine belonging to the Platelet Differentiation Growth Factor (PDGF) family, and existing as a disulfide-linked homodimeric glycoprotein. In contrast to the longer isoforms, VEGF-A121 is more freely diffusible, and cannot bind to heparin. In vivo, VEGF is expressed predominantly in lung, heart, kidney, and adrenal glands, and the expression of VEGF is up-regulated by a number of growth factors, including PDGF, Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF), Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF), and Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF). VEGF signals via binding to two tyrosine kinase receptors: the Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (Flt-1) and the kinase domain receptor (KDR). VEGF is a specific mitogen and survival factor, contributing to abnormal angiogenesis and cancer development.
-

VEGF164, Mouse
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) was initially purified from media conditioned by normal bovine pituitary folliculo-stellate cells and by a variety of transformed cell lines as a mitogen specific for vascular endothelial cells. It was subsequently found to be identical to an independently discovered vascular permeability factor (VPF), which was previously identified in media conditioned by tumor cell lines based on its ability to increase the permeability of capillary blood vessels. Three mouse cDNA clones, which arise through alternative splicing and which encode mature mouse monomeric VEGF having 120, 164, or 188, amino acids, respectively, have been identified. Two receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), Flt-1 and Flk-1 (the mouse homologue of human KDR), both members of the type III subclass of RTKs containing seven immunoglobulin-like repeats in their extracellular domains, have been shown to bind VEGF with high affinity. The roles of the homodimers of KDR, Flt, and the heterodimer of KDR/Flt in VEGF signal transduction remain to be elucidated. In vivo, VEGF has been found to be a potent angiogenesis inducer.
-

VEGF164, Rat (CHO-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor A164 (VEGF-A164), a member of the cysteine knot growth factor, is one of major isoforms of VEGF-As. VEGF-As are endothelial cell-specific mitogens with angiogenic and vascular permeability-inducing properties. During maturation, rat VEGF-A is alternatively spliced to generate rVEGF-A120, rVEGF-A164 and rVEGF-A188 which correspond to hVEGF-A121, hVEGF-A165 and hVEGF-A189 in human, respectively (the numbers designate the amino acid residues). The active form of rVEGF-A164 is either a homodimeric or heterodimeric polypeptides which bind to the transmembrane tyrosine kinases receptors FLT1, FLK1 or KDR or to the non-tyrosine kinase neuropilin receptors NRP1/2.
-

VEGF165, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) is a potent growth and angiogenic cytokine. It stimulates proliferation and survival of endothelial cells, and promotes angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Expressed in vascularized tissues, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) plays a prominent role in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Substantial evidence implicates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in the induction of tumor metastasis and intra-ocular neovascular syndromes. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) signals through the three receptors; fms-like tyrosine kinase (flt-1), KDR gene product (the murine homolog of KDR is the flk-1 gene product) and the flt4 gene product.
-

VEGF165, Human(HEK 293-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) is a potent growth and angiogenic cytokine. It stimulates proliferation and survival of endothelial cells, and promotes angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Expressed in vascularized tissues, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) plays a prominent role in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Substantial evidence implicates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in the induction of tumor metastasis and intra-ocular neovascular syndromes. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) signals through the three receptors; fms-like tyrosine kinase (flt-1), KDR gene product (the murine homolog of KDR is the flk-1 gene product) and the flt4 gene product.
-
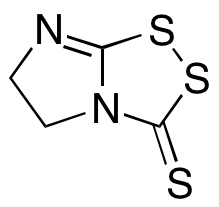
Vegita
$683.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H4 N2 S3
-
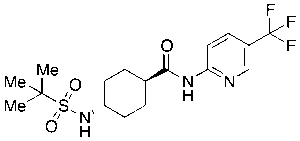
Velneprit
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H24F3N3O3S
-
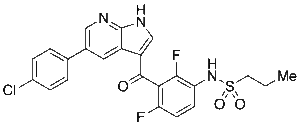
Vemurafenib
$83.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H18 Cl F2 N3 O3 S
-
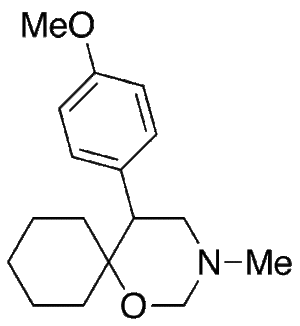
Venlafaxine Cyclic Impurity
$1,606.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H25 N O2
-

Venlafaxine-d6 N-Oxide
$1,710.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H21D6NO3
-

Verapamil Ethyl Methanethiosulfonate, Bromide
$374.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H45 N2 O6 S2 . Br
-

Verapamil-d3 Hydrochloride
$323.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 D3 H35 N2 O4 . Cl H
-

Verapamil-d6
$2,286.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 D6 H32 N2 O4
-
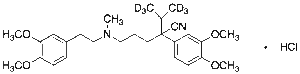
Verapamil-d6 Hydrochloride
$1,967.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 2H6 H32 N2 O4 . Cl H
-

Veratramine
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H39 N O2
-
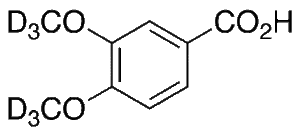
Veratric Acid-d6
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H4D6O4
-
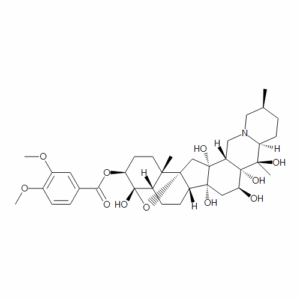
Veratridine
$188.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C36 H51 N O11
-

Veratridine
$184.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsVeratridine
-
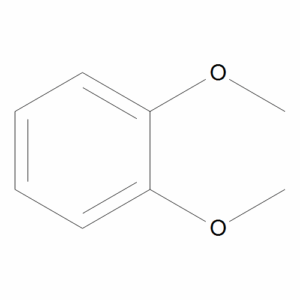
Veratrole
$62.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H10 O2






